Essential Guidelines and Considerations for Horse Breeding
Breeding horses can be an exciting and rewarding endeavor for equestrians and horse enthusiasts alike. It allows for the preservation and improvement of desired traits, the development of superior-performance animals, and the continuation of valuable bloodlines. However, successful horse breeding requires careful planning, thorough knowledge, and responsible decision-making. In this blog post, we will discuss some important factors to keep in mind when breeding your horse.
Define Your Breeding Goals
Before initiating the breeding process, it is crucial to establish clear objectives and breeding goals. Determine what you hope to achieve with the offspring – whether it’s enhancing specific traits, improving performance capabilities, or preserving a particular bloodline. Having well-defined goals will guide your selection of suitable breeding stock and help you make informed decisions throughout the process.
Breeding horses without a clear purpose or market demand can lead to oversupply and difficulties in finding suitable homes for the offspring. Avoid breeding without a well-defined breeding goal and an understanding of the market demand for the specific breed or type of horse you are producing.
Selecting Compatible Horses

One of the crucial aspects of horse mating is selecting compatible horses. Consider the following factors:
- Breed: Ensure that the horses you choose for mating are of the same breed or compatible breeds that complement each other. Indian horse breeds like Marwari, Kathiawari, Manipuri, and Spiti are often bred within their respective breeds to preserve and promote their unique characteristics and traits.
- Bloodline: Thoroughly researching bloodlines is vital to understand the strengths and weaknesses of potential breeding stock. A well-informed decision based on comprehensive research can significantly increase the chances of breeding successful offspring.
- Health and Conformation: Select horses that are in good health, free from any genetic disorders, and possess desirable conformation traits suitable for the breed.
- Temperament: Assess the temperament of both the stallion and the mare. Compatible temperaments can contribute to successful breeding and easier handling of the offspring. If a mare has a bad temperament, there is a possibility that she may pass on some of those traits to her offspring. Given the high heritability of temperament, it may be worth reconsidering breeding from a mare with a challenging riding temperament.
Choosing the Right Stallion

When selecting a stallion for breeding, there are several qualities and factors to consider. Here are some key qualities that are often desirable in a stallion:
- Conformation: A stallion should have good overall conformation, including well-balanced proportions, correct limb structure, strong musculature, and appropriate breed-specific traits. Conformation influences the horse’s soundness, movement, and overall athleticism, which can be passed on to the offspring.
- Pedigree and Bloodlines: The stallion’s pedigree and bloodlines are important considerations. Studying the lineage can provide insights into the stallion’s genetic potential, including any notable ancestors with successful performance records or desirable traits. A stallion from a well-established and reputable breeding program may also carry more value.
- Performance Record: The stallion’s performance record in the discipline or area of interest can be an indicator of his abilities and genetic potential. Successful competition results or achievements in relevant disciplines can demonstrate desirable traits that may be passed on to his offspring.
- Trainability: A stallion should possess a good temperament, displaying a willing and trainable nature. A calm and cooperative stallion is generally easier to handle and work with, making the breeding process safer and more manageable for both the horse and handlers. Positive temperament traits can also be inherited by the foals.
- Fertility: A comprehensive veterinary examination and fertility assessment should be conducted to ensure the stallion is capable of successfully breeding and producing viable semen.
- Proven Progeny: Evaluating the stallion’s existing offspring can provide valuable insights into his ability to pass on desirable traits. Observing the conformation, performance, and temperament of his foals can help gauge the stallion’s genetic influence and the potential quality of future offspring.
Timing is the Key
Familiarize yourself with the estrus cycle of mares, as timing is crucial for successful mating. The mare’s reproductive cycle typically lasts 21 days, with ovulation occurring around the 14th to 16th day. Mating should take place during the fertile period, which is usually two to three days before ovulation.
Look for signs of estrus, including frequent urination, raised tail, winking of the vulva, and increased receptiveness to the stallion’s advances. Consider using hormone assays or veterinary assistance to confirm estrus and optimize timing.
Reproductive Health and Veterinary Care

Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Pre-Breeding Examinations: Conduct thorough reproductive health examinations for both the mare and the stallion, including assessments of fertility, breeding soundness, and contagious diseases.
- Vaccinations and Deworming: Ensure that both horses are up to date on vaccinations and deworming protocols to minimize the risk of diseases and maintain overall health.
- Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule routine check-ups throughout the gestation period to monitor the mare’s health, detect any potential issues, and provide appropriate prenatal care.
Breeding Management and Training
Ensure that the stallion is well-trained for breeding procedures and behaves appropriately during the mating process. He should be familiar with mounting a breeding mount or phantom for artificial insemination, as well as proper handling and restraint during natural covering. Regularly exercising the stallion typically leads to enhanced vitality (libido) and improved fertility.
Proper Transportation
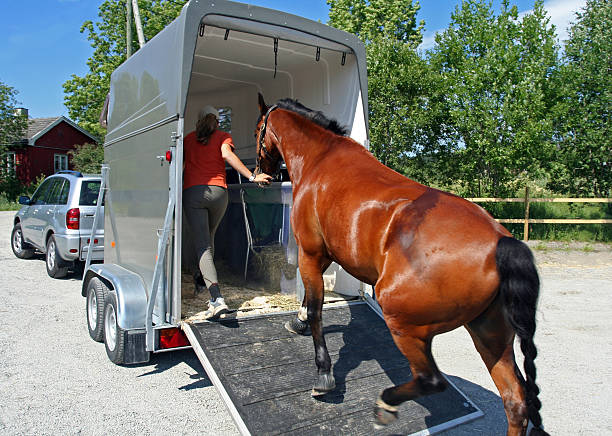

It is of utmost importance to prioritize the safety of the horse at all times, especially during transportation in the breeding process. It is common for mares to be transported to the farm of the horse breeder. When transporting your horse, whether to a breeding facility or another location, it is crucial to ensure proper loading and securement in the trailer to maintain its safety throughout the journey.
- Adequate Trailer Selection: Choose a trailer that is appropriate for the size and needs of your horse. Ensure that the trailer is well-maintained, in good condition, and equipped with suitable safety features such as secure dividers, non-slip flooring, and sufficient ventilation.
- Proper Loading: Take the time to properly load the horse into the trailer. Use a calm and patient approach, ensuring that the horse enters willingly and is comfortable inside. Avoid rushing or forcing the horse, as this can lead to stress or injury.
- Secure the Horse Inside the Trailer: Once the horse is inside the trailer, ensure it is properly secured to prevent any unnecessary movement or injury during transit. Use appropriate tying methods and ensure the partitions and dividers are in place to prevent the horse from shifting its weight or becoming unbalanced.
- Monitor the Horse During Transport: Regularly check on the horse’s well-being during transportation. Stop periodically to provide water and allow the horse to rest, stretch its legs, and relieve itself. Ensure the trailer is well-ventilated and maintain a comfortable temperature inside.
- Drive Responsibly and Safely: As the driver, it is your responsibility to operate the towing vehicle and trailer safely. Adhere to all traffic regulations and drive cautiously, especially when maneuvering or braking, to minimize stress and jolts to the horse. Avoid sudden turns, accelerations, or abrupt stops that may cause the horse to lose balance or sustain injuries.
- Unloading the Horse: When reaching the destination, follow a careful unloading procedure. Open the trailer doors calmly and safely, ensuring there are no obstructions or hazards outside. Allow the horse to exit at its own pace, encouraging it with a gentle voice and positive reinforcement.
Prepare the Environment

Proper preparation for mating is crucial to ensure a safe and conducive breeding environment.
- Breeding Facility: Create a safe and comfortable breeding environment, such as a breeding shed or a controlled pasture, which allows for better management and minimizes distractions.
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Ensure that both the stallion and mare are clean and free from any potential sources of infection. Regular cleaning of the genital area is essential for maintaining hygiene.
Mating Techniques
When it comes to horses, two primary breeding techniques are utilized- natural mating and artificial insemination.
- Natural Cover: Natural mating involves allowing the mare and stallion to interact directly for breeding. They are introduced to each other, and the stallion mounts the mare for mating.
- Artificial Insemination (AI): Alternatively, consider AI techniques, which offer several advantages such as reducing the risk of injury, managing transportation logistics, and increasing the number of mares a stallion can breed with. Consult with a veterinarian experienced in equine reproduction for guidance on AI procedures.
Introducing the Stallion
When it comes to natural mating, introducing the stallion to the mare requires caution and careful management. Initially, it is advisable to let the horses become acquainted while separated by a secure barrier or through controlled interactions in a controlled environment. This allows them to establish a level of comfort and familiarity before direct contact. Always prioritize the safety of both horses and have experienced handlers present to minimize the risk of injury.
Teasing of Mare

In the context of horse breeding, teasing refers to the process of introducing a mare to a stallion to assess her estrus (heat) cycle and determine if she is receptive to mating. The teasing process typically involves bringing the mare near the stallion, either in a controlled environment or by allowing them to see, hear, and smell each other from a safe distance in teasing stall. The purpose is to observe the mare’s behavior and physical signs of estrus to determine the optimal time for mating. Without conducting teasing it’s not possible for the horse breeder to understand the heat cycle of a mare.
The duration of the teasing process can vary depending on the mare’s cycle and the breeder’s specific goals and preferences. Some breeders may conduct teasing sessions over several days, while others may extend it for a week or longer. The duration of a teasing session may vary from 5 to 20 minutes, depending on the mare and the chosen teasing method. The frequency of teasing sessions can also vary, ranging from once or twice a day to every few days, depending on the mare’s behavior and the breeder’s observations.
During teasing, the breeder will carefully monitor the mare’s response to the stallion. Signs of estrus that the breeder looks for include the mare lifting her tail, winking her vulva, urinating, vocalizing, or showing signs of increased receptivity and interest in the stallion. Once the mare consistently displays these signs, indicating that she is in peak estrus and receptive to mating, the breeder can proceed with the actual mating.
Monitor the Mating Process
During natural mating, it is crucial to carefully observe the breeding process to ensure proper alignment and successful mating. The mare should be in a standing heat position, and the stallion should mount her from the correct side. If difficulties arise or the horses are not mating successfully, consult with a veterinarian or experienced breeder for guidance. They can provide assistance and may recommend further intervention, such as using artificial insemination if natural mating proves unsuccessful.
Post-Mating Care
Post-mating care should be considered to optimize the chances of successful conception and the health of the mare.
- Rest and Monitoring: After mating, provide the mare with adequate rest and minimal exercise. The mare should be closely monitored after breeding to ensure she does not show any signs of discomfort or complications. Regular observations should be made to check for any signs of injury, infection, or abnormal behavior.
- Pregnancy Confirmation: Around 14 to 16 days after mating, consult a veterinarian for pregnancy confirmation through ultrasound or other appropriate methods.
- Adjusting Management Practices: As the pregnancy progresses, adjustments may be needed in the mare’s management, feed, and exercise routine. This may involve gradually reducing the intensity of exercise, providing appropriate bedding and shelter, and ensuring the mare is kept in a safe and stress-free environment. Please refer to our blog on caring for a pregnant horse to gain knowledge about the appropriate care for a pregnant mare.

Do’s and Don’ts of Breeding Horse
Do’s
- Only engage experienced and trained handlers during the breeding process. Inexperienced individuals may not have the necessary skills to read horse behavior or react appropriately in potentially high-risk situations. Handlers should have a good understanding of horse body language, be able to anticipate reactions, and have the ability to intervene when necessary.
- Be vigilant and attentive to warning signs or behavioral cues exhibited by the horses during the mating process.
- Be patient with the horses; it might take a lot of effort and energy, however, the rewards of this patience are well worth it when it comes to achieving successful breeding outcomes.
Don’ts
- Avoid aggressive or forceful mating practices, as they can result in injuries to both the mare and the stallion. Horses have natural behaviors and instincts during mating, and it’s crucial to allow them to proceed naturally. Forcing the process can lead to physical harm and cause psychological distress.
- Don’t breed horses with underlying health issues or conditions that may pose a risk during the mating process. Ensure that both the mare and the stallion are in good overall health and free from contagious diseases.
- Avoid rushing or skipping important preparatory steps, such as proper estrus detection and timing, pre-breeding examinations, and reproductive health assessments. Adequate preparation allows for better planning and reduces the risk of complications during the mating process.

Seek Expert Advice
Consulting with experienced breeders, trainers, and equine professionals can provide invaluable guidance and insight. They can offer advice on suitable pairings, potential risks, and the overall breeding process. Learn from their experiences, seek mentorship, and consider joining breed associations or forums where you can interact with fellow breeders and enthusiasts. Manu Sharma, a renowned YouTube vlogger, and owner of a stud farm, is widely recognized for sharing informative content on the subject of horse breeding. To delve deeper into the realm of horse breeding, we recommend exploring Manu Sharma’s channel, where you can find a wealth of valuable information through his engaging videos.
Conclusion
Breeding horses is an art that demands knowledge, dedication, and meticulous attention to detail. Remember, each breeding endeavor is unique, and the journey is as important as the destination. Embrace the joy of creating new life and continuously expand your knowledge to refine your breeding program and contribute to the future of the equine industry.